Promise 学习笔记(一)
一直有在用 Promise,但是没有系统学过 Promise,自然也不知道原理。现在就来学习一波。
1. 介绍
Promise 是 JS 中进行异步编程的新解决方案。在这之前使用过回调函数进行异步编程。
Promise 是一个构造函数,Promise 对象用来封装一个异步操作并可以获取其成功或失败的结果值
Promise 优点
支持链式调用,可解决回调地狱问题
回调地狱:回调函数嵌套使用

**回调地狱导致的问题**:
- 指定回调函数的方式更灵活
- Promise:启动异步任务 => 返回 Promise 对象 => Promise 对象绑定回调函数
- 纯用回调函数:必须在启动异步任务前指定
2. Promise 体验
2.1 抽奖
先来一个抽奖示例(隔 1s 后出结果)
2.1.1 回调函数版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Promise初体验</title>
</head>
<body>
<button class="btn" id="btn">抽奖</button>
<script>
function rand() {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * 100 + 1);
}
const btn = document.querySelector("#btn");
btn.addEventListener("click", function () {
setTimeout(() => {
let n = rand();
if (n <= 50) {
alert("恭喜你中奖了");
} else {
alert("很遗憾,你没有中奖");
}
}, 1000);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|

2.1.2 Promise 版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Promise初体验</title>
</head>
<body>
<button class="btn" id="btn">抽奖</button>
<script>
function rand() {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * 100 + 1);
}
const btn = document.querySelector("#btn");
btn.addEventListener("click", function () {
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let n = rand();
setTimeout(() => {
if (n <= 50) {
resolve(n);
} else {
reject(n);
}
}, 1000);
});
p.then(
(value) => {
alert(`恭喜你,中奖了,中奖号码是${value}`);
},
(value) => {
alert(`真遗憾,你没有中奖,中奖号码是${value}`);
}
);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
2.2 文件读取
2.2.1 回调函数版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| const fs = require("fs");
fs.readFile("./resource/content.txt", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
console.log(data.toString());
});
|
2.2.2 Promise 版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
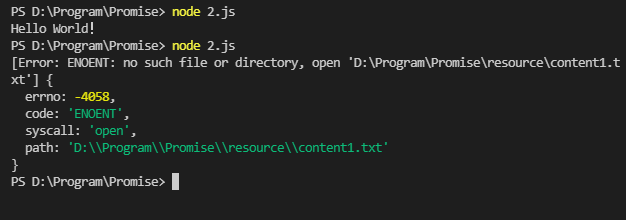
| const fs = require("fs");
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile("./resource/content1.txt", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
reject(err);
} else {
resolve(data);
}
});
});
p.then(
(value) => {
console.log(value.toString());
},
(reason) => {
console.log(reason);
}
);
|
2.3 AJAX
2.3.1 原生版本(回调函数)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Promise封装AJAX</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
(function () {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("GET", "https://qcgx2i.api.cloudendpoint.cn/hello");
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
console.log(xhr.response);
} else {
console.log(xhr.status);
}
}
};
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
|

2.3.2 Promise 版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Promise封装AJAX</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
(function () {
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("GET", "https://qcgx2i.api.cloudendpoint.cn/hello");
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
resolve(xhr.response);
} else {
reject(xhr.status);
}
}
};
});
p.then(
(data) => {
console.log(data);
},
(statusCode) => {
console.warn(statusCode);
}
);
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
3. 转化为 Promise 风格(promisify)
**util.promisify()**:传入一个遵循常见的错误优先的回调风格的函数(即以 (err, value) => {...}作为最后一个参数),并返回 Promise 版本。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| const fs = require("fs");
const { promisify } = require("util");
let pReadfile = promisify(fs.readFile);
pReadfile("./resource/content.txt").then((value) => {
console.log(value.toString());
});
|
4. Promise 属性
4.1 Promise 状态
实例对象中的一个属性 [[PromiseState]],有三个值
- pending:未决定
- resolved(fulfilled):成功
- rejected:失败
Promise 的状态改变只有两种可能,且只能改变一次:
- pending 变为 resolved
- pending 变为 rejected
成功的结果数据一般称为 value,失败的结果一般称为 reason
4.2. Promise 对象的值
实例对象中的一个属性 [[PromiseResult]],保存着异步任务成功或失败的结果
只能通过resolve()或reject()对 PromiseResult进行修改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| const fs = require("fs");
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile("./resource/content1.txt", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
reject(err);
} else {
resolve(data);
}
});
});
p.then(
(value) => {
console.log(value.toString());
},
(reason) => {
console.log(reason);
}
);
|
5. Promise 工作流程

6. Promise API
6.1 构造函数 Promise(excutor)
excutor 函数:执行器, (resolve, reject) => {}
resolve 函数:内部定义成功后调用的函数
reject 函数:内部定义失败后调用的函数
构造函数会在 Promise 立即同步调用,异步操作在执行器中执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(1);
});
console.log(2);
|
6.2 Promise.prototype.then 方法
语法: promise.then(onResolved, onRejected)
onResolved 函数:成功的回调函数, value => {}
onRejected 函数:失败的回调函数, reason => {}
返回新的 Promise 对象
6.3 Promise.prototype.catch 方法
**与上面的 then()类似,不过只能指定失败的回调函数
6.4 Promise.resolve 方法
作用:接受一个参数,返回一个成功或失败的 Promise 对象。能够快速封装一个值,将这个值转化为 Promise 对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| const p1 = Promise.resolve(123);
console.log(p1);
const p2 = Promise.resolve(p1);
console.log(p2);
const p3 = Promise.resolve(
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject("Error");
})
);
p3.catch((reason) => {
console.log(reason);
});
|
6.5 Promise.reject 方法
接受一个参数,返回一个失败的 Promise 对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| const p1 = Promise.reject(123);
console.log(p1);
const p2 = Promise.reject(
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("传参为成功的Promise对象");
})
);
console.log(p2);
|

6.5 Promise.all 方法
参数:promises,promise 的数组
返回一个新的 Promise,当所有的 promise 都成功才成功,且结果为成功的结果组成的数组;有一个失败就直接失败,返回的结果就是失败的那一个的结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("p1: OK");
});
const p2 = Promise.resolve("p2: OK");
const result1 = Promise.all([p1, p2]);
console.log(result1);
const p3 = Promise.resolve("p3: OK");
const p4 = Promise.reject("p4: Err");
const p5 = Promise.reject("p5: Err");
const result2 = Promise.all([p3, p4, p5]);
console.log(result2);
|

如果想要捕捉异常,直接链式调用即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| const p3 = Promise.resolve("p3: OK");
const p4 = Promise.reject("p4: Err");
const p5 = Promise.reject("p5: Err");
const result2 = Promise.all([p3, p4, p5]);
console.log(result2);
result2.catch((reason) => {
console.log(reason);
});
|

Promise.all()传入一个空数组,立即返回成功。
6.6 Promise.race 方法
参数:promises,promise 的数组
返回一个新的 Promise,第一个完成的结果是成功则成功,反之则失败
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("p1: OK");
});
});
const p2 = Promise.reject("p2: Err");
const result1 = Promise.race([p1, p2]);
console.log(result1);
result1.catch((reason) => {
console.log(reason);
});
|
Promise.race()传入空数组不做任何操作
本次学习是视频学习:尚硅谷 Web 前端 Promise 教程从入门到精通











